For example, a manufacturing company purchases a machine on Dec. 1, 2019 for $56,000. If a company buys an asset for $5000 and expects to sell it for $1000 in three years, it can then depreciate $4000. At the end of three years, the company expects to sell the asset for $1000.
- On the other hand, intangible assets are non-physical assets that gradually reduce value over a given period of time through amortization.
- Suppose you are buying an asset through instalments or loan payments and you make a deposit.
- In Tally, fixed assets refer to assets like land, buildings, machinery, etc., used for long-term business operations and not meant for sale.
- The asset value will be reduced with a credit and a loss will be recognized for the reduction of value.
- Another classification of fixed assets is that they are non current assets; thereby, they are not expected to be easily converted into cash.
- To accurately determine the Net Income (profit) for a period, incremental depreciation of the total value of the asset must be charged against the same period’s revenue.
ASC 360 requires annual impairment analysis for all long-lived assets to test for significant changes in an asset’s fair market value and if the costs related to the asset are recoverable. Current assets refer to company-owned items that will be converted into cash within the year. Long-term assets are the remaining items that can’t be replaced with cash within one year.
Tax
Certain assets may be used until they are worthless and are disposed of without remuneration, while others may still have value to the business at the end of their service life. Most tangible assets, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, are depreciated. However, land cannot be depreciated because it cannot be depleted over time unless it contains natural resources. Fixed assets are used by the company to produce goods and services and generate revenue. With the exception of land, fixed assets are depreciated to reflect the wear and tear of using the fixed asset. They can be depreciatedWith the exception of land, fixed assets are depreciated to reflect the wear and tear of using the fixed asset.
- While this may seem obvious to some of you, not registering correct records of your fixed assets can cause some real headaches.
- Businesses can maximize the value and efficiency of fixed assets through effective asset management, regular maintenance, upgrades, and optimization of asset utilization.
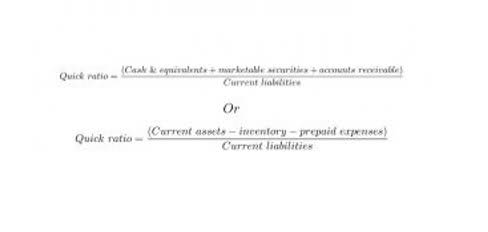
- Current assets are assets that can be converted into cash within one fiscal year or one operating cycle.
- This category includes cash, accounts receivable, and short-term investments.
- Since values for some assets change frequently, revaluation can happen as often as once a year.
- Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of the asset to operations over the estimated useful life of the asset.
Generally speaking, the more revenue your business generates, the higher the capitalisation policy. This is to save yourself time in the calculations and also to make it easier to keep an overview of your costs. These assets, like buildings, machinery, and equipment, provide value year after year, helping businesses grow and thrive. Managing them wisely can lead to efficiency and success (and tax deductions!). Your balance sheet shows the assets and liabilities owned by your business.
What Is a Fixed Asset in Accounting? With Examples
Yes, companies can lease or rent fixed assets instead of purchasing them outright, which provides flexibility and may have tax advantages. Fixed assets are initially recorded at cost and subsequently depreciated or amortized over their useful lives. They are valued on the balance sheet at historical cost, net of depreciation or impairment. As accounting standards continuously evolve and converge, the differences between IFRS and GAAP may decrease over time. However, it is crucial for companies operating in multiple jurisdictions to be aware of these variations and comply with the appropriate accounting standards for their financial reporting.

It can tell readers of financial statements if a large purchase of fixed assets may be coming in the near future or if fixed assets are being managed well. Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable (AR), inventory, and prepaid expenses. Aside from fixed assets and intangible assets, other types of noncurrent assets include long-term investments.
What are Fixed Assets ?
These procedures include documenting financial records, calculating revenue, estimating fixed-asset valuations and complying with tax laws. Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures (GAAP) form the standard used by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). An asset is any resource that you own or manage with the expectation that it will yield continuing benefits or cash flows. An asset is also a resource the value of which you can dependably measure.
Form 424B2 BARCLAYS BANK PLC – StreetInsider.com
Form 424B2 BARCLAYS BANK PLC.
Posted: Tue, 14 Nov 2023 19:18:03 GMT [source]
In the case of asset grouping, one or multiple assets included in an asset group may be transferred. The treatment of operating lease ROU assets, however, is quite different from fixed assets and the related ROU asset is amortized using a different method. Generally, the higher https://www.bookstime.com/ the fixed asset turnover ratio, the more efficient the company is since it implies more revenue is created per dollar of fixed assets owned. The accounting treatment of “depreciating” certain intangible assets is conceptually identical to depreciating tangible assets.
Under U.S. GAAP reporting, fixed assets are typically capitalized and expensed across their useful life assumption on the income statement. Fixed assets are non-current assets on a company’s balance sheet and cannot be easily converted into cash. Examples of current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
The acquisition or disposal of a fixed asset is recorded on a company’s cash flow statement under the cash flow from investing activities. The purchase of fixed assets represents a cash outflow (negative) to the company while a sale is a cash inflow (positive). fixed asset accounting examples If the asset’s value falls below its net book value, the asset is subject to an impairment write-down. This means that its recorded value on the balance sheet is adjusted downward to reflect that it is overvalued compared to the market value.
Example of Tangible fixed Assets
Yet, they report purchasing and other related costs on the balance sheet. Public companies that file quarterly and annual reports to the SEC must present their financial statements in accordance with GAAP,” Adams says. Fixed assets are fixed in nature and cannot be easily convertible into cash. They provide the necessary resources for generating income and can also be used as collateral for loans. GAAP refers to the accounting principles, standards, and procedures used in the United States. It is established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and is the standard framework for financial reporting in the U.S.

